Over time, you may have noticed that excess fat in your abdomen could potentially be hiding a critical issue—your body’s insulin sensitivity. This hidden organ, often overlooked, plays a pivotal role in regulating your blood sugar levels. Understanding how to address this problem is vital for your health, as it could lead to improved energy and a lower risk of serious conditions like diabetes. In this post, we’ll research into the intricacies of this hidden organ and provide practical solutions to help you regain control.
Key Takeaways:
- The book emphasizes the role of visceral fat as a hidden organ that impacts blood sugar regulation and overall health, highlighting its different effects compared to subcutaneous fat.
- It presents actionable strategies for reducing visceral fat through dietary changes, exercise, and lifestyle adjustments, aiming to promote better blood sugar control and overall wellness.
- The author advocates for a shift in mindset regarding fat, presenting it as a dynamic and influential component of health rather than merely a substance to eliminate.
The Obscure Role of Visceral Fat in Blood Sugar Regulation
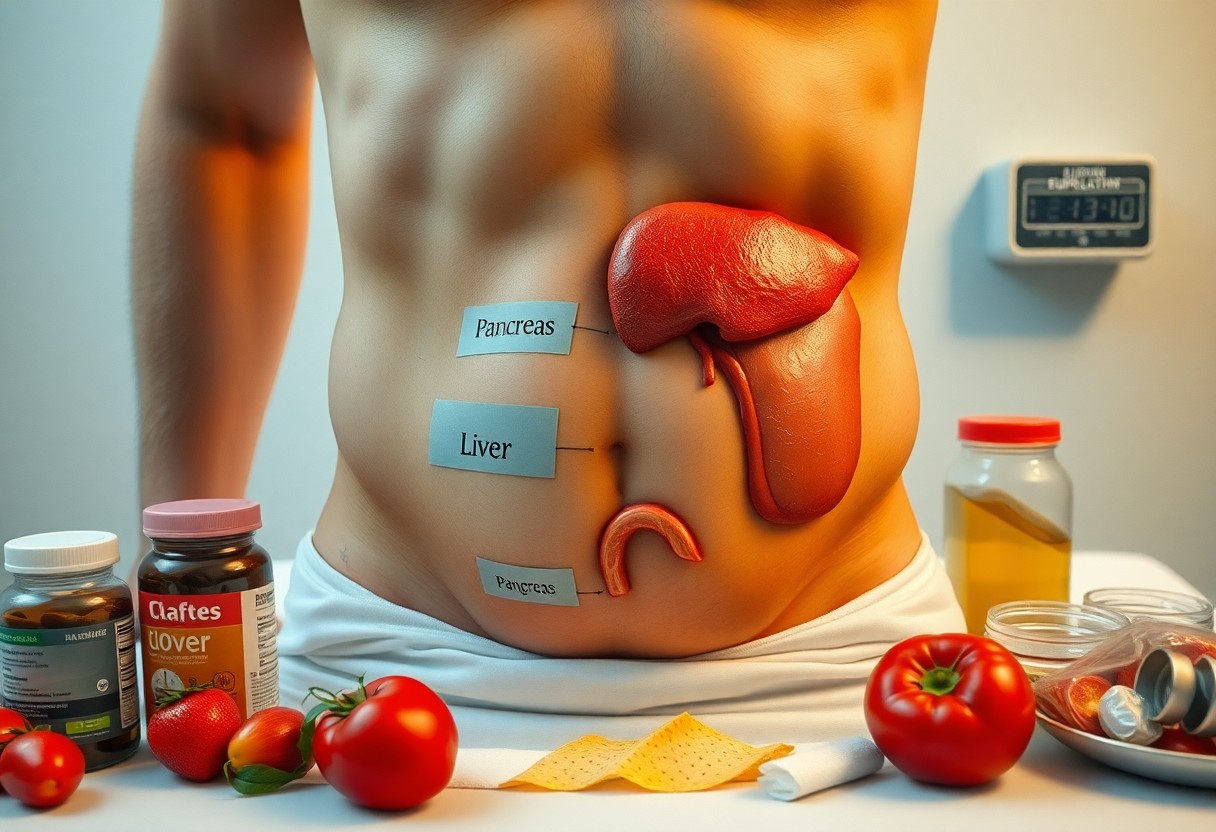
Visceral fat, often dubbed the “hidden fat,” plays a significant role in your overall metabolic health, especially in regulating your blood sugar levels. Unlike subcutaneous fat, which sits just under the skin, visceral fat is stored deep within your abdomen, surrounding vital organs. This makes it particularly dangerous as it can lead to insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and even cardiovascular issues. Understanding how visceral fat affects your body’s dynamics could be the key to unlocking better health and achieving stable blood sugar levels.
Understanding Visceral Fat: The Metabolic Time Bomb
Visceral fat acts as a metabolic time bomb due to its unique ability to release inflammatory substances directly into your bloodstream. This type of fat is particularly responsive to hormonal changes and can affect your body’s normal functions. In fact, just a few extra pounds of this dangerous fat can significantly increase your risk of developing chronic illnesses, creating a vicious cycle of poor health and disrupted metabolism.
How Visceral Fat Influences Insulin Sensitivity
Your body’s insulin sensitivity is heavily influenced by the amount of visceral fat you carry. Increased visceral fat leads to higher levels of free fatty acids and inflammatory markers, which can impair your ability to respond to insulin effectively. The result? Your cells become less receptive to insulin, causing your blood sugar levels to rise. Unfortunately, this can set off a cascade of metabolic disruptions, further exacerbating weight gain and increasing the risk of developing diabetes.
For instance, research shows that even a modest increase in visceral fat can lead to a 50% decrease in insulin sensitivity for some individuals. This means that the body struggles to utilize glucose properly, leaving you with elevated blood sugar levels that can wreak havoc on your health. Addressing visceral fat through a combination of diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes is vital to restoring your insulin sensitivity and achieving balance in your metabolism.
The Connection Between Gut Health and Blood Sugar Control
Your gut health plays a significant role in regulating blood sugar levels. A balanced microbiome can enhance insulin sensitivity and help you maintain stable glucose levels. In contrast, an imbalanced gut can lead to inflammatory responses and insulin resistance, both of which contribute to erratic blood sugar spikes. Optimizing your gut health through diet and lifestyle changes can provide a valuable strategy for managing your blood sugar and overall well-being.
The Gut Microbiome: Your Body’s Hidden Ally
The gut microbiome consists of trillions of microorganisms that live in your digestive tract, collaborating to support digestion and metabolic processes. These diverse microbes aid in breaking down complex carbohydrates and produce short-chain fatty acids, which can improve insulin sensitivity. Maintaining a diverse and balanced gut microbiome enhances nutrient absorption and promotes metabolic health, highlighting its vital role in blood sugar regulation.
Dysbiosis and Its Impact on Glucose Metabolism
Dysbiosis occurs when there is an imbalance in your gut microbiome, leading to an overgrowth of harmful bacteria and a reduction in beneficial species. This disruption can result in increased intestinal permeability, often referred to as “leaky gut.” This permeability allows toxins to enter the bloodstream, triggering inflammation and promoting insulin resistance, which can impede your body’s ability to effectively regulate blood glucose levels.
The link between dysbiosis and glucose metabolism is supported by research indicating that individuals with type 2 diabetes often exhibit altered gut microbiota composition. Specific strains of beneficial bacteria, like Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, have been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation. In contrast, an overabundance of opportunistic pathogens can lead to chronic inflammation, thereby exacerbating glucose intolerance. Microbiome-focused interventions, such as dietary changes or probiotics, may help restore gut health and mitigate insulin resistance, ultimately improving your glucose metabolism.
Unpacking the Hormonal Interplay: Cortisol, Hormones, and Blood Sugar
The intricate relationship between hormones and blood sugar management is pivotal for maintaining optimal health. As you navigate the maze of hormonal influences, understanding the dynamics of cortisol and other hormones can provide you with insight into how your body processes glucose. When hormonal balance is disrupted, your blood sugar levels can escalate or plummet, leading to potential health complications. The connectedness of these systems reveals why addressing hormonal health is fundamental in your quest for stable blood sugar levels.
Stress and Blood Sugar: The Cortisol Connection
Elevated stress levels trigger the release of cortisol, a hormone known for its role in the body’s fight-or-flight response. As cortisol levels spike, your body aims to provide a quick source of energy, resulting in increased glucose production by the liver. This can create a cycle of soaring blood sugar levels, contributing to insulin resistance over time. Monitoring your stress is crucial: chronic stress not only keeps cortisol high but also sets the stage for long-term blood sugar management issues.
The Role of Adipokines in Glucose Homeostasis
Adipokines, which are cell-signaling proteins produced by fat tissue, play a key role in regulating your glucose levels and insulin sensitivity. Among these, leptin and adiponectin have significant impacts; while leptin helps manage energy expenditure, adiponectin enhances insulin sensitivity and promotes glucose metabolism. An imbalance of these signals, often resulting from excess visceral fat, can impede glucose homeostasis, leading to type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders. By reducing visceral fat through healthier lifestyle choices, you can improve adipokine production and support stable blood sugar levels.
Actionable Strategies to Reverse Metabolic Dysfunction
Implementing effective strategies to combat metabolic dysfunction can dramatically improve your health and well-being. Start by paying attention to your diet, increasing your physical activity, and prioritizing restorative sleep. These fundamental changes can work synergistically to help manage your blood sugar levels, reduce visceral fat, and enhance your overall metabolic function. You have the power to shift your body towards a healthier state, reclaiming your energy and vitality.
Diet Overhaul: Foods That Fight Visceral Fat
Incorporating nutrient-dense foods into your diet can significantly help reduce visceral fat. Focus on whole, unprocessed options such as leafy greens, berries, and healthy fats like avocados and olive oil. Foods high in fiber, such as legumes and whole grains, not only regulate blood sugar but also keep you feeling full longer. Additionally, lean protein sources like fish and chicken promote muscle maintenance, necessary for boosting metabolism.
The Importance of Physical Activity and Sleep
Regular physical activity and adequate sleep are two cornerstones of metabolic health that greatly influence visceral fat levels. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise weekly, combined with strength training twice a week, can optimize insulin sensitivity and help shed excess fat. Sleep, on the other hand, plays a critical role in hormone regulation and energy balance. Aiming for 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly ensures your body has the chance to repair and maintain proper metabolic function.
Creating a consistent routine that includes physical activity and restorative sleep can profoundly impact your health. Activities like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling elevate your heart rate, facilitating effective fat loss while strengthening your cardiovascular system. Moreover, incorporating strength training not only builds muscle but also enhances resting metabolism. Meanwhile, making sleep a priority is necessary, as studies indicate that inadequate sleep can lead to increased hunger hormones like ghrelin, complicating your efforts to manage weight. Balancing both physical activity and restorative sleep ultimately fosters a resilient metabolism, allowing you to reclaim control over your health.
The Future of Blood Sugar Management: Innovations on the Horizon
Emerging solutions are reshaping how we approach blood sugar management, emphasizing personalization and technology. As understanding of metabolic health grows, new tools and therapies will help you maintain stable glucose levels through tailored approaches. With these innovations, you can expect more efficient, user-friendly, and effective strategies that empower you to take control of your health.
Emerging Technologies in Glucose Monitoring
Recent advancements in glucose monitoring are revolutionizing how you track your blood sugar. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) with real-time data delivery enable you to understand your glucose trends throughout the day, facilitating timely adjustments to your diet and lifestyle. Moreover, future devices promise additional features like smartphone integration and predictive analytics to forecast glucose fluctuations, significantly enhancing your management capabilities.
The Promising Role of Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine is set to reshape your approach to blood sugar management. As genetic and metabolic profiles become more accessible, tailored interventions based on individual responses to treatments will emerge. This means therapies and dietary recommendations can be customized according to your unique needs. For instance, individuals may receive specific carbohydrate intake guidance or targeted medications from genetic tests, greatly improving overall management and outcomes.
The shift towards personalized medicine emphasizes the importance of understanding your individual metabolic profile. By analyzing factors such as genetic predispositions, lifestyle habits, and even microbiome composition, healthcare providers can tailor recommendations specifically to you. This precision approach not only maximizes the effectiveness of treatments but can also minimize the risk of adverse reactions, making you an active participant in your health journey. Furthermore, the integration of wearable technology will support ongoing assessments, keeping you informed about how your body responds and allowing for real-time adjustments to optimize glucose management.
To wrap up
Upon reflecting on the role of fat in your body, particularly the hidden organ that influences your blood sugar levels, it’s clear that understanding how to manage this can significantly impact your health. By adopting a balanced diet, incorporating regular exercise, and being mindful of stress, you can support your body in regulating blood sugar more effectively. Taking proactive steps to address fat in undesirable areas can empower you to lead a healthier, more balanced life.
FAQ
Q: What is the central theme of ‘Fat in All the Wrong Places’?
A: The book highlights how specific fat storage in the body, particularly around the liver and abdominal area, is associated with insulin resistance and blood sugar issues. It emphasizes that the location of fat distribution is more significant than the overall amount of fat in the body. Understanding how this hidden organ, often overlooked, affects your blood sugar levels is vital for managing health effectively.
Q: How can one identify if they are affected by the issues discussed in the book?
A: The book provides various indicators to help identify if one might be struggling with the hidden organ issue. Common signs include unexplained fatigue, weight gain around the abdomen, increased cravings for sugary foods, difficulty managing blood sugar levels, and a family history of diabetes. It encourages readers to assess their lifestyle, diet, and any symptoms that may point to the underlying problems associated with fat storage and insulin sensitivity.
Q: What solutions or strategies does the book offer for fixing blood sugar issues?
A: ‘Fat in All the Wrong Places’ offers practical strategies such as dietary changes, including the reduction of processed sugars and refined carbs, incorporating regular exercise, and managing stress levels. It emphasizes the importance of a balanced diet rich in whole foods, fiber, and healthy fats. Additionally, the book suggests monitoring blood sugar levels regularly and working closely with healthcare professionals to develop a tailored plan for improving overall metabolic health.